Let’s get to know HIV, a virus that attacks the immune system, leading to immune deficiency and causing AIDS. It can be a significant cause of mortality. However, individuals with HIV who receive treatment are referred to as “people living with HIV.” Only those whose immune systems have significantly weakened, resulting in opportunistic infections, are classified as “AIDS patients.” This means that not everyone with a positive HIV Status will progress to AIDS. The outcome depends on timely treatment and the individual’s adherence to care and healthy practices.
HIV Status and Symptoms
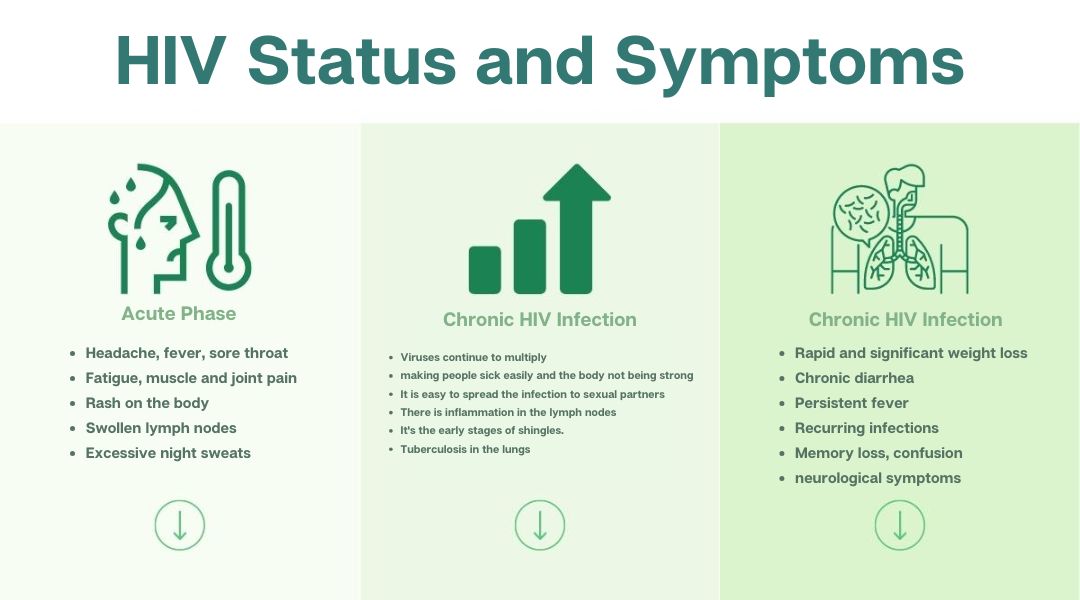
Not everyone with HIV will show symptoms in the early stages. Here are some common signs that may occur:
Early Stage of HIV Infection or Acute Phase

- Headache, fever, sore throat
- Fatigue, muscle and joint pain
- Rash on the body
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Excessive night sweats
These symptoms may resemble those of other viral infections, such as the flu, and often appear 2-4 weeks after exposure to HIV. It is essential to prioritize getting tested if you experience these symptoms and have a high-risk history of exposure.
Chronic HIV Infection or Clinical Latency Stage
Advanced HIV Infection or AIDS Stage
If individuals are unaware of their HIV status and do not receive proper medical treatment, the infection may progress to AIDS. At this stage, the immune system is severely weakened, leaving the body highly susceptible to severe infections or opportunistic diseases. The overall health of the individual deteriorates significantly. Common symptoms of advanced HIV infection include.

- Rapid and significant weight loss
- Chronic diarrhea
- Persistent fever
- Recurring infections
- Lesions or sores on the skin or inside the mouth
- Memory loss, confusion, or neurological symptoms
HIV Status Testing
To detect HIV infection, various testing methods are currently available. Here are some of the most common types of HIV tests:
Antibody-HIV Test
- This widely used method detects antibodies produced by the body in response to HIV. Blood samples are typically used, but oral fluids or urine samples can also be tested in some cases. It’s important to note that it may take up to a month for the body to produce enough antibodies for the test to detect. If the initial test result is negative but there is still suspicion of HIV exposure, it is recommended to retest after an appropriate period, usually around three months.
Antigen-HIV Test
- This test detects antigens, which are substances produced by the virus itself. It can identify HIV infection earlier than the antibody test since antigens appear in the bloodstream sooner. This method is often combined with the antibody test to provide more accurate results.
Nucleic Acid Test – NAT
- NAT is a highly sensitive and precise test that detects the nucleic acids (RNA) of the HIV virus. This method can identify HIV infection as early as 5-7 days after exposure, even before antibodies or antigens are detectable. NAT is commonly used for early diagnosis in cases of high risk or suspected acute HIV infection.
Benefits of Knowing Your HIVStatus
Knowing whether you are HIV-positive or negative helps reduce the risk of spreading HIV to others and offers several other advantages, including:
HIV Status Enables Prompt Treatment
Detecting HIV in its early stages allows for timely medical intervention, including the initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART can suppress the virus, reduce its replication, and prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS due to immune system decline. Early treatment significantly improves the long-term health outcomes for individuals with HIV.
HIV Status Improves Treatment Outcomes
Being aware of your HIV status enables regular monitoring of your viral load (the amount of virus in the blood) and CD4 count (a key indicator of immune system health). Routine health checks and lab tests help track disease progression and allow healthcare providers to address any emerging health issues effectively.
HIV Status Promotes Safe Sexual Practices
Knowing you are HIV-positive empowers you to take precautions to prevent transmitting the virus to partners, such as consistently and correctly using condoms. If you are HIV-negative, this knowledge helps you take proactive steps to protect yourself and remain free of the virus.

Prevents Mother-to-Child Transmission
Pregnant women who know their HIV status can take measures to prevent transmitting the virus to their unborn child. Proper medical care and treatment from a healthcare team can significantly reduce the risk of mother-to-child transmission, ensuring the health and well-being of both mother and baby.
Provides Access to Support and Resources
Awareness of your HIV status allows you to seek support from specialized healthcare providers, HIV/AIDS organizations, and support groups for people living with HIV. These resources can offer valuable information, counseling, and assistance in managing the physical, emotional, mental health, and social aspects of living with HIV. By knowing your HIV status, you can take control of your health, protect those around you, and access the support needed to live a full and meaningful life.
Related Articles
Last Updated on 26/12/2025 by ทีมที่ปรึกษา มูลนิธิเพื่อรัก

