HIV is a virus that directly affects the body’s immune system, particularly CD4 white blood cells, which play a crucial role in protecting the body against pathogens and infections. Without proper treatment, the immune system becomes weakened, increasing the risk of opportunistic infections and serious illnesses such as tuberculosis, pneumonia and certain cancers. However, with modern medical advancements, people living with HIV can enjoy good health and lead normal lives if they take proper care of their health. Boosting the immune system is a key factor in helping the body fight off infections, reduce the risk of complications and enhance overall quality of life. This article will provide information on how to strengthen immunity for people living with HIV — from proper use of antiretroviral therapy (ART), good nutrition, regular exercise, and quality sleep, to effective stress management — so that you can take charge of your health and live a long, healthy life.
Why Boosting Immunity Is Important for People Living with HIV
The immune system is the body’s primary defense against various pathogens. However, when the body is infected with HIV, the virus attacks and destroys CD4 white blood cells — a crucial part of the immune system that helps protect against infections. When CD4 levels drop too low, the immune system becomes weakened, making the body more vulnerable to opportunistic infections and other complications.

The Impact of a Weakened Immune System
When the immune system is compromised, people living with HIV may experience more health issues, such as:
Signs of a Weakened Immune System:
- Feeling unusually fatigued
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent colds or infections
- Mouth sores or slow-healing wounds
- Night sweats without a clear cause
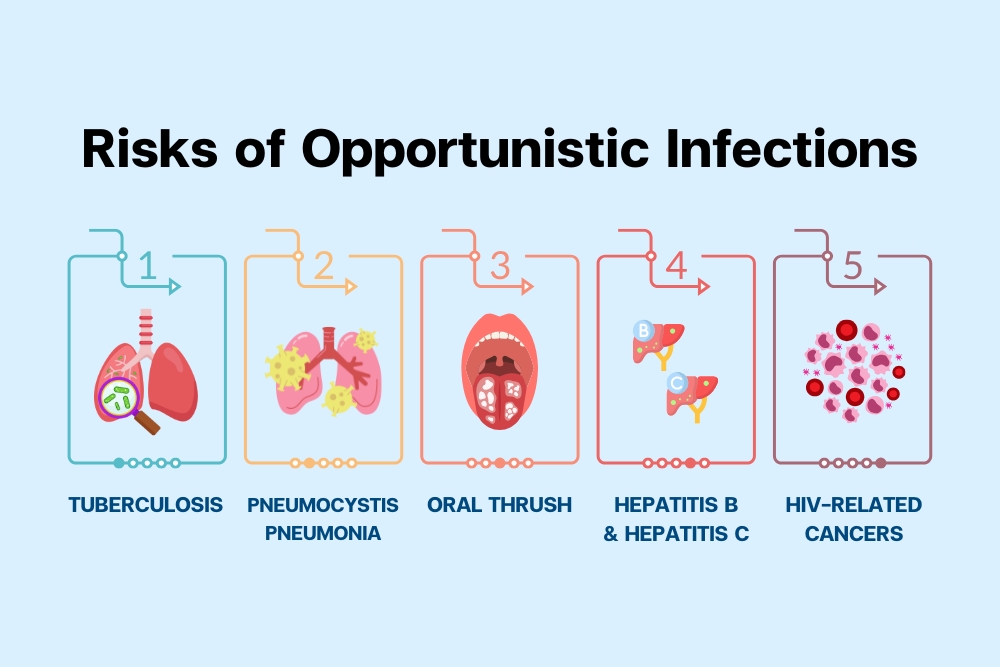
Risks of Opportunistic Infections
- Tuberculosis (TB): A common infectious disease in people with weakened immune systems.
- Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP): A severe lung infection often found in people with untreated HIV.
- Oral Thrush: A fungal infection in the mouth and throat, causing white patches and pain while eating.
- Hepatitis B and C (HBV & HCV): These viruses can cause chronic liver inflammation and increase the risk of liver cirrhosis.
- HIV-related Cancers: Such as lymphoma and cervical cancer.
How Immune Support Works to Boost Immunity with HIV?
Boosting the immune system is crucial for helping people with HIV stay healthy and live a normal life. The benefits of immune support include:
- Reducing the Risk of Opportunistic Infections
- A stronger immune system helps the body better defend against infections, lowering the chances of complications.
- Faster Recovery from Illness
- With proper nutrition, regular exercise, and sufficient rest, the body can recover more quickly from infections and illness.
- Improved Energy and Quality of Life
- A stronger immune system helps increase energy, reduce fatigue, and improve the ability to perform daily activities.
- Enhanced Effectiveness of Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
- A well-functioning immune system supports the effectiveness of ART, helping to better control the viral load.
10 Ways to Boost Immunity for People Living with HIV
Strengthening the immune system is essential for people living with HIV because the virus directly affects immune function, weakening the body and increasing the risk of opportunistic infections. However, with proper health care, people with HIV can live a strong, healthy life. Here are 10 key ways to boost immunity for those living with HIV:

1. Take Antiretroviral Medication Consistently
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the primary method for controlling the HIV viral load and keeping the immune system strong. When taken correctly, ART can reduce the viral load to undetectable levels, lowering the risk of complications. Missing even a few doses can lead to drug resistance and a rebound in viral levels, significantly impacting immune health.
👉 Tips:
- Take your medication at the same time every day
- Use reminder apps or set alarms
- Talk to your doctor if you experience side effects
2. Eat a Nutritious Diet
Good nutrition supports immune health and helps the body stay strong. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients needed for immune cell repair and function.
🍽 Recommended Foods:
- High-quality proteins: eggs, fish, chicken, beans, tofu
- Vitamin C (citrus fruits) and Vitamin D (salmon, sunlight)
- Zinc (nuts, pumpkin seeds)
🚫 Foods to Limit or Avoid:
- Foods high in sugar and trans fats
- Excessive alcohol and caffeine
3.Exercise Regularly
Physical activity improves circulation and strengthens the immune system.
🏃♂️ Recommended Activities:
- Light cardio: brisk walking, swimming, cycling
- Strength training: weight lifting to build muscle
- Yoga and meditation to relieve stress
Exercise not only boosts immunity but also helps the body manage stress more effectively.
4. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking and drinking alcohol can weaken the immune system.
🚭 Negative Effects:
- Increases the risk of lung and heart diseases
- Reduces the effectiveness of ART
👉 How to Quit:
- Use nicotine replacement products like gum
- Avoid triggers that encourage alcohol consumption
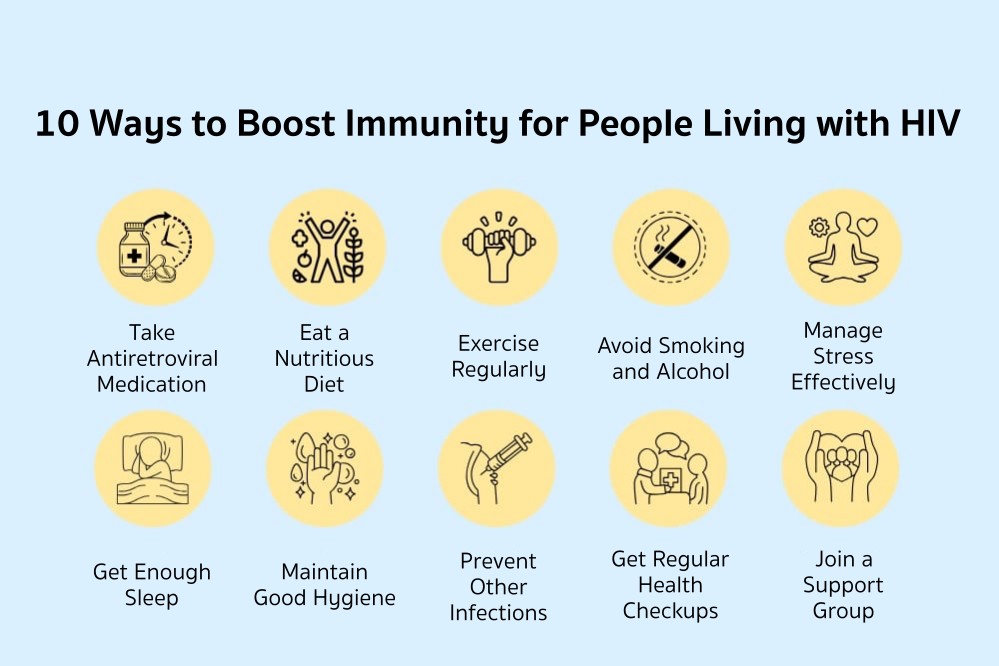
5. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress negatively impacts the immune system. Finding healthy ways to manage stress helps maintain physical well-being.
🧘♀️ Stress Reduction Tips:
- Practice meditation and yoga
- Listen to music or read your favorite books
- Talk to friends or join a support group
6. Prevent Other Infections
Due to a weakened immune system, people with HIV are more susceptible to other infections.
💉 Important Prevention Tips:
- Get vaccinated for the flu and hepatitis B
- Wash hands frequently to prevent bacterial and viral infections
- Avoid close contact with individuals who have contagious illnesses
7. Get Enough Sleep
Quality sleep helps the body recover. Lack of rest can weaken immune function and increase the risk of infections.
💤 Better Sleep Tips:
- Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep per night
- Avoid caffeine and screen time before bed
- Create a calm and quiet sleep environment
8. Maintain Good Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene significantly reduces the risk of infections by keeping the body clean and protected.
🛁 What You Should Do:
- Wash your hands often, especially before meals
- Brush and floss regularly to prevent gum disease
- Avoid raw or undercooked foods
9. Get Regular Health Checkups
Routine medical visits allow for health monitoring and timely medical advice.
🏥 Key Actions:
- Blood tests to monitor CD4 count and viral load
- Regular dental and eye exams
- Screenings for other infections like TB and hepatitis
10. Join a Support Group
Having a supportive social network improves mental health and confidence in managing HIV.
🤝 Benefits of Support Groups:
- Gain advice from others with lived experience in managing HIV, including medication and mental health
- Reduce stress and anxiety, and encourage healthy behaviors
Preventing Other Infections That Can Affect the Body
People living with HIV are at higher risk of opportunistic infections compared to the general population. This is because the HIV virus weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off germs. Therefore, preventing other infections is crucial for maintaining health and improving quality of life.
Essential Vaccinations
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent infectious diseases. Vaccines can reduce the risk of illnesses that may have a severe impact on those with weakened immune systems.

💉 Recommended Vaccines:
Influenza Vaccine: Should be taken annually to reduce the risk of seasonal flu, which can be more severe in those with weakened immunity.
- Pneumococcal Vaccine: Helps prevent bacterial infections that can cause pneumonia, a common and serious illness in people with HIV.
- Hepatitis B Vaccine: People with HIV are at higher risk of contracting hepatitis B, which can lead to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Hepatitis A Vaccine: Protects against a virus that can harm the liver.
- HPV Vaccine (Human Papillomavirus): Reduces the risk of cervical cancer and other cancers linked to HPV.
- Shingles Vaccine: Recommended for individuals over 50 to prevent shingles, which can be more severe in immunocompromised people.
📌 Note: Always consult a doctor before getting vaccinated, as some vaccines may not be suitable for individuals with very low CD4 counts.
Maintaining Good Hygiene
Preventing infections starts with practicing good hygiene in everyday life.
🧼 Hygiene Tips to Reduce the Risk of Infection:
- Wash your hands regularly with soap and clean water, or use alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Keep your body clean by showering daily and wearing clean clothes.
- Maintain oral hygiene: brush your teeth twice a day, floss regularly, and visit the dentist for routine checkups.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who are sick, such as those with colds, the flu, or respiratory infections.


Choosing Safe and Clean Food
Unclean or undercooked food can lead to gastrointestinal infections, which may be more severe for people with weakened immune systems.
🥗 Safe Eating Tips:
- Eat freshly cooked food and avoid raw or undercooked items such as sushi or raw eggs.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating.
- Avoid expired food or items that have been stored for a long time.
- Use clean water for cooking, and drink only filtered or boiled water.
Avoiding Insects and Disease-Carrying Animals
Some insects and animals can carry pathogens that may lead to serious illnesses, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
🐜 Prevention Tips:
- Use mosquito nets and repellents to protect against diseases like dengue and malaria.
- Avoid contact with pets that may carry infections, such as birds, cats, or wild animals that could transmit fungi or parasites.
- Wash your hands after handling animals or cleaning animal cages.


Practicing Safe Sex
Unprotected sex can increase the risk of acquiring other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which may further impact the health of people living with HIV.
❤️ Protection Tips:
- Always use condoms during sexual activity.
- Limit the number of sexual partners to reduce the risk of infection.
- Get tested regularly for sexually transmitted infections.
Preventing Tuberculosis (TB) and Other Opportunistic Infections
Tuberculosis is one of the most common infections in people living with HIV. Therefore, TB prevention is a crucial part of HIV care.
🩺 Prevention Tips:
- Get screened for TB regularly, especially if experiencing symptoms such as a persistent cough, unexplained weight loss, or night sweats.
- If diagnosed with latent TB infection, preventive medication may be needed to stop it from progressing.
- Avoid high-risk environments, such as crowded places with poor ventilation.


Reducing the Use of Immunosuppressive Drugs and Harmful Substances
Certain medications or substances can negatively affect the immune system, especially in people living with HIV.
💊 Cautionary Guidelines:
- Avoid using steroids or immunosuppressive drugs unless absolutely necessary.
- Refrain from using recreational drugs or excessive alcohol, as they can weaken the body.
- Always consult a doctor before taking any medication to avoid negative effects on immune function.
Related Articles
- Unveiling the Importance of CD4 Cells in Immune Health
- How to support people with HIV & prevent new infections?
Strengthening the immune system is essential for people living with HIV, as the virus directly affects the body’s immunity. A strong immune system reduces the risk of complications and helps individuals live a normal, healthy life.
“Key approaches to boosting immunity include strictly adhering to antiretroviral therapy (ART), which lowers the viral load and prevents drug resistance. This should be combined with a nutritious diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins that help repair cells and strengthen immune defenses. Regular exercise supports better blood circulation, reduces stress, and enhances overall strength. Adequate sleep plays a crucial role in cellular recovery and immune function. Managing stress is equally important, as chronic stress can weaken the immune system over time.”
Another critical factor is preventing additional infections through essential vaccinations, practicing good hygiene, and engaging in safe sex to reduce exposure to other pathogens. Avoiding smoking and alcohol also helps the body maintain stronger immune defenses. While living with HIV can be challenging, proper health care and following recommended guidelines can enable people with HIV to live long, healthy, and fulfilling lives. Balanced living, following medical advice, and taking care of your overall well-being are the keys to staying confident and safe in your journey with HIV.
✨ Always take care of your health — because a strong body is the key to a quality life! 💪💙
Reference:
โภชนาการสำหรับผู้ติดเชื้อเอชไอวี
- gj.mahidol.ac.th/main/knowledge-2/nutrition-for-hiv-patients/
การกินอาหารเสริมหรือผลิตภัณฑ์ต่างๆ เพื่อเพิ่มเซลล์ภูมิต้านทาน
- thaiaidssociety.org/news/taking-dietary-supplements-or-products-to-increase-cd4-immune-cells-in-hiv-infected/
HIV กับโภชนาการและความปลอดภัยด้านอาหาร
- hivinfo.nih.gov/understanding-hiv/fact-sheets/hiv-and-nutrition-and-food-safety
Last Updated on 18/12/2025 by ทีมที่ปรึกษา มูลนิธิเพื่อรัก

