Gonorrhea infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in Thailand, particularly among teenagers and working-age adults who engage in unprotected sex. This infection is caused by bacteria that can easily spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sexual contact. Without proper medical treatment, gonorrhea can lead to serious complications affecting the reproductive system and may even cause infertility in the future.
Although gonorrhea is a curable disease, many people misunderstand the condition—some believe it will go away on its own, while others self-medicate without consulting a doctor. These actions not only delay recovery but also increase the risk of antibiotic resistance and transmission to others. This article provides essential guidance from medical experts to help you understand the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and proper treatment of gonorrhea infection, along with practical advice on prevention and self-care.
What Is Gonorrhea Infection?
Gonorrhea infection is classified based on the type of bacteria causing the disease. The primary form, known as true gonorrhea, is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, while chlamydial infection—often called non-gonococcal urethritis—is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis.


The two infections differ mainly in their incubation periods. Chlamydial infection tends to develop more slowly, and in individuals with strong immune systems, symptoms may not appear for several weeks or even months. This makes it difficult to recognize the infection early. Because of this, gonorrhea and related infections can be dangerous if left untreated. They not only damage the reproductive system but also increase the risk of contracting other sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea Infection
The symptoms of gonorrhea infection can vary between men and women, and in some cases, people may show no signs at all. However, recognizing the early symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
In women
common symptoms include:

- Irregular menstrual periods
- Burning sensation or pain during urination
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal discharge with a strong odor
- Vaginal bleeding between periods or after sex
- Itching or irritation around the genital area
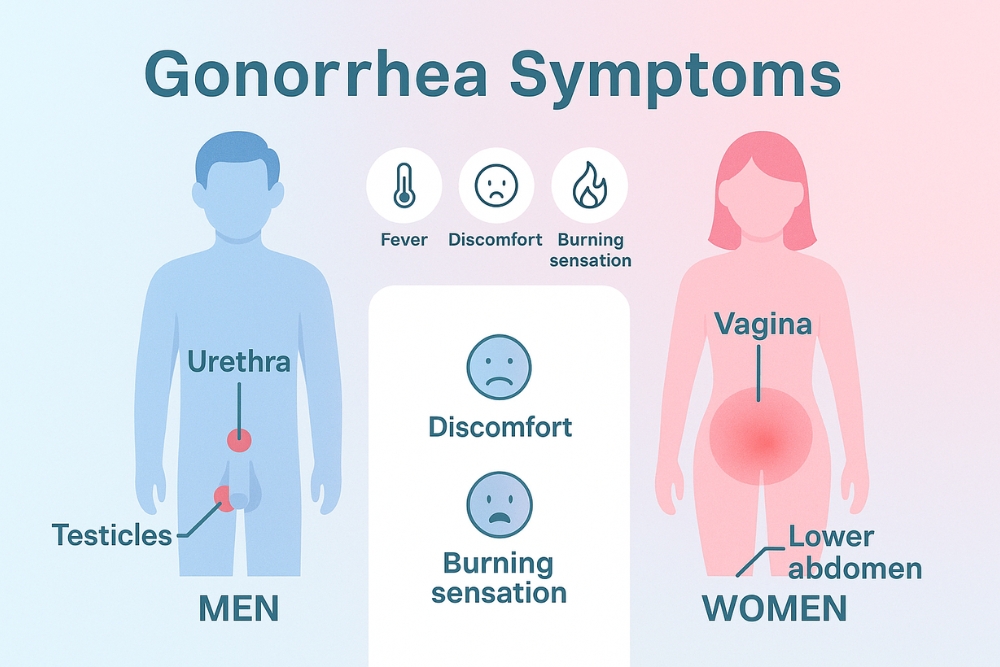
In men
symptoms may include:
- Thick, yellow or greenish discharge from the tip of the penis
- Inflammation or swelling of the foreskin
- Pain or tenderness in one or both testicles
- Burning or pain during urination
- Clear or cloudy mucus discharge from the urethra
In both men and women, the symptoms may appear within a few days after exposure, but in some cases, they can take several weeks to manifest. Anyone who experiences these signs should seek medical advice immediately for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How Is Gonorrhea Infection Treated?
Many people mistakenly believe that gonorrhea infection can heal on its own — and while symptoms may sometimes subside temporarily, the infection rarely goes away without proper medical treatment. If you suspect you have gonorrhea, it is essential to seek care from a qualified healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Before beginning treatment, the doctor will assess your risk factors and medical history. Laboratory tests are then used to confirm the infection. There are two common testing methods:
- Swab Test – A sterile swab is used to collect samples of bodily fluids from areas such as the genitalia, cervix, rectum, throat, or urethra. These samples are then examined in a laboratory to identify the presence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis.
- Urine Test – For men, a urine sample is collected to detect bacterial DNA. It is recommended not to urinate for at least two hours before testing to ensure an accurate result, as fresh urination may wash away bacterial traces.
Both gonorrhea and chlamydial infections can be cured with antibiotics—either oral or injectable—prescribed by a doctor. However, antibiotic resistance is becoming a growing concern, which makes it critical to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and complete the entire course of medication. Patients are also advised to have their sexual partners tested and treated at the same time to prevent reinfection. After completing treatment, it is best to return for a follow-up test to confirm that the infection has completely cleared.
What Happens If Gonorrhea Infection Is Left Untreated?
If gonorrhea whether caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae (true gonorrhea) or Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydial infection)—is left untreated, the bacteria can spread and lead to serious complications that differ between men and women. These complications can cause long-term damage to the reproductive system and, in severe cases, result in infertility.
Complications in Men
Epididymitis or Prostatitis
- The infection may spread to the epididymis, testicles, or prostate gland, leading to pain, swelling, fever, fatigue, and discomfort in the groin area. If left untreated, it can cause testicular atrophy, reduced sperm production, and even permanent infertility.
Reiter’s Syndrome (Reactive Arthritis)
- Some patients may develop inflammation in the joints due to an autoimmune response. Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, fatigue, weight loss, and enlarged lymph nodes. Without treatment, joint mobility may decrease over time.
Conjunctivitis (Eye Infection)
- Bacteria from genital secretions can spread to the eyes, causing redness, irritation, swelling of the eyelids, blurred vision, or discharge of yellow pus. The infection often starts in one eye and may spread to the other if not treated promptly.
Complications in Women
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Untreated gonorrhea can spread to the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, fever, nausea, and bleeding after intercourse. Severe cases may lead to scarring of the reproductive organs, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy or infertility.
Bartholin’s Gland Infection
Bacterial infection of the Bartholin’s glands—located near the vaginal opening—can lead to swelling, pain, or cyst formation. If untreated, it may cause significant discomfort, especially during walking or sexual intercourse, and in rare cases, may develop into cancer.
Vaginitis (Vaginal Inflammation)
This condition causes itching, irritation, and abnormal discharge that may appear green, gray, or white, often accompanied by a fishy odor. Symptoms typically worsen after sexual intercourse or urination.
Salpingitis (Inflammation of the Fallopian Tubes)
The infection may block the fallopian tubes, leading to inflammation and pain in the lower abdomen, especially during sex or menstruation. Spotting, abnormal discharge, and frequent urination are also common.
Newborn Eye Infection
Pregnant women with gonorrhea can pass the infection to their babies during childbirth, leading to severe conjunctivitis in newborns. Without immediate treatment, this condition can cause blindness.

Can Condoms Prevent Gonorrhea Infection?
Yes — using condoms correctly and consistently is one of the most effective ways to prevent gonorrhea infection. Condoms act as a physical barrier that reduces direct contact with infected bodily fluids, lowering the risk of transmission by up to 90%. They are affordable, easy to find at convenience stores, and have no side effects when used properly. To ensure maximum protection, it’s important to choose the right condom size, check the expiration date, and store them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Avoid using oil-based lubricants, which can damage latex, and use water-based lubricants instead.
In addition to condom use, it’s highly recommended to get screened for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) at least once a year—or sooner if you have new or multiple sexual partners. Early detection allows for timely treatment and helps prevent spreading the infection to others. Self-medicating or assuming the infection will go away on its own is dangerous and can make treatment more difficult in the long run. Always seek medical care from a qualified doctor or sexual health clinic to receive proper diagnosis and antibiotic treatment tailored to your condition.
Conclusion
Gonorrhea infection may seem minor to some, but it is a serious sexually transmitted disease that requires prompt attention. If left untreated, it can cause severe reproductive complications in both men and women and increase the risk of other infections. The best way to protect yourself is to get tested and treated by healthcare professionals as soon as symptoms appear. Effective treatment with the right antibiotics can cure gonorrhea completely. However, long-term prevention requires safe sexual practices—such as using condoms consistently, undergoing regular STI check-ups, and maintaining open, honest communication with sexual partners. By taking these steps, you can safeguard your health, prevent reinfection, and enjoy a safe and confident sex life.
References:
↪︎ โรคหนองใน (Gonorrhea) อาการ สาเหตุ การตรวจวินิจฉัย
↪︎ โรคติดเชื้อระบบสืบพันธุ์น่ารู้: โรคหนองใน
↪︎ หนองในหายเองได้ไหม เกิดขึ้นได้อย่างไร เป็นได้ทั้งชายและหญิง
Last Updated on 17/12/2025 by ทีมที่ปรึกษา มูลนิธิเพื่อรัก

