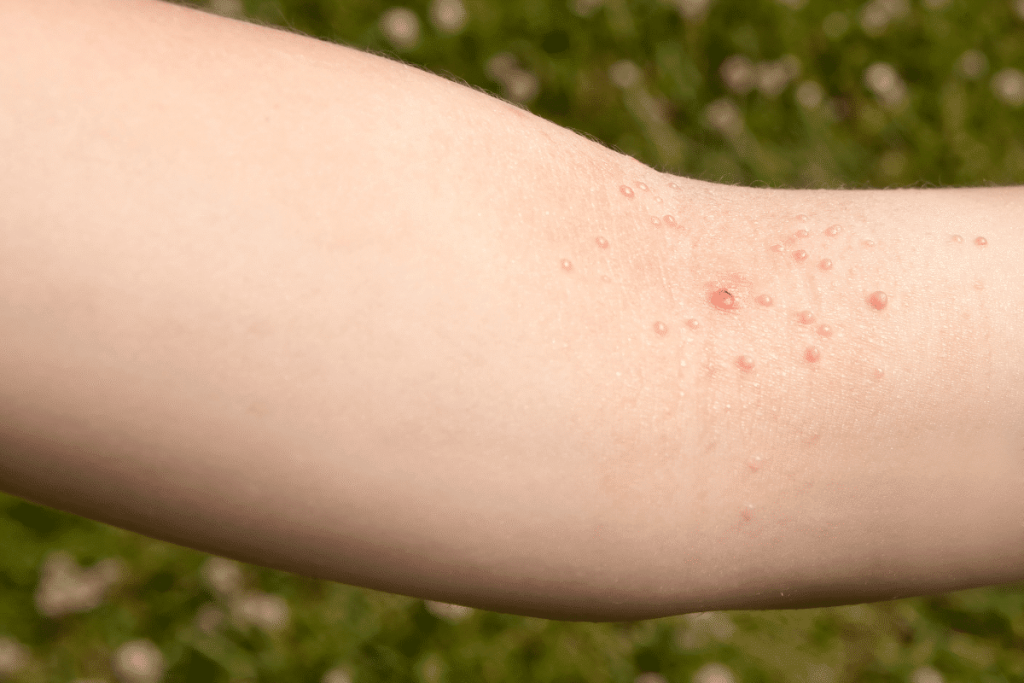
Another relatively common sexually transmitted infection (STI) the molluscum contagiosum virus. This virus can spread through skin-to-skin contact and by sharing personal items such as towels.
kin infection is caused by a virus called Molluscum contagiosum. Symptoms include small, painless bumps around the genitals. If a person who is infected with this virus scratches the bumps or if the bumps are injured, the infection can spread to other skin areas.
If I do have molluscum contagiosum, how do I know?
As mentioned before, visible signs of molluscum contagiosum is the appearance of bumps on the skin. You may have molluscum contagiosum if you experience bumps that match the description below:
- Bumps that re flesh colored. They are raised and round.
- The diameter of the biggest bump is less than 6 millimeters.
- You can see a tiny dot near the center of each bump.
- Sometimes the bumps can be red and inflamed.
- Itchiness (but this is not always the case)
- Should a person contract this virus through sexual contact, the bumps will appear on their genitals, lower abdomen, and inner upper thighs.
Keep in mind that your immune system is also a determining factor for any signs and symptoms of molluscum contagiosum. The bumps may be if you have a weak immune system
How does MCV spread?
Unlike other STIs such as HIV, which is strictly transmitted through unprotected sex and sharing needles, molluscum contagiosum can be easily spread from the following:
- Skin-to-skin contact. Hugging, kissing, and holding hands with a person who is infected with molluscum contagiosum.
- Sharing personal items that are contaminated with the virus such as toothbrushes, razors, and towels.
- Sexual contact with a person who is infected with the virus.
How do I prevent molluscum contagiosum from spreading?
- Washing your hands regularly and thoroughly. Washing your hands frequently and carefully can lower the chance of the virus spreading.
- Do not share personal items. Any personal items that can touch your skin such as towels and toothbrush might be contaminated with the virus. You should also avoid borrowing these items from other people as you may not know whether they have the infection or not.
- Avoid any sexual contact. If you have the virus and you can see bumps as described above, do not have sex until they are treated and have completely disappeared. Also avoid having sex with a partner who has bumps on their genitals. Bear in mind that condoms may only cover certain parts of the genitals (i.e. the penis) and the bumps may appear on other areas as well so condoms will not protect you from MCV.
- Do not scratch or rub the bumps. This is because you will spread the virus to other skin areas. This also means that you should not shave the areas where the bumps appear (or even when they appear near the areas that are infected).
Can molluscum contagiosum be easily treated?
While the bumps may be annoying and cause inconvenience, fortunately molluscum contagiosum can be treated easily and, in general, it will not cause any complications.