Warts from HPV are a common skin condition that many people are familiar with. While they are generally not life-threatening, these warts can cause discomfort, affect self-confidence, and in some cases, signal an infection linked to more serious diseases such as cervical cancer or anal cancer. The primary cause of warts is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), a virus with more than 100 different strains that can easily spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or unprotected sexual activity.
Understanding Warts from HPV is therefore crucial — from their causes and symptoms to treatment and prevention. With proper awareness and timely medical care, the risks of complications can be significantly reduced, helping you protect both your health and overall quality of life.
What Are Warts and What Causes Them?
Warts from HPV are abnormal growths of the skin that appear as small, hard bumps. They may be the same color as the skin or appear brown, gray, or even black depending on their type and location. The main culprit is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), which enters the body through tiny cuts or abrasions on the skin.

While most HPV strains are harmless, certain high-risk types — such as HPV-16 and HPV-18 — are strongly linked to serious cancers, including cervical cancer, oral cancer, throat cancer, and anal cancer. This is why warts should never be dismissed as a minor skin issue; in some cases, they may serve as an important warning sign of more severe underlying conditions.
Types of Warts
Warts can develop in different parts of the body. They are generally divided into two major groups: skin warts and mucosal warts. Below are the common types of skin warts caused by HPV:
1. Skin Warts
- Common Warts
- Caused mainly by HPV types 2 and 4. These warts appear as hard, rough, raised bumps that are often round but irregular. They range in size from 1–10 millimeters and may be flesh-colored, gray, brown, or black. Although harmless and non-cancerous, they can be unsightly and sometimes uncomfortable. They commonly appear on the hands, fingers, knees, elbows, or even the face. They can spread through direct contact with the wart or indirectly via contaminated personal items such as towels, shoes, or razors.
- Flat Warts
- Caused by HPV types 3, 10, 28, and 49. These are small, flat, and smooth bumps, often flesh-colored or slightly brownish. They are usually found in clusters on the face, neck, arms, or backs of the hands. Flat warts do not cause pain but can be distressing due to cosmetic concerns, especially when they appear on visible areas like the face.
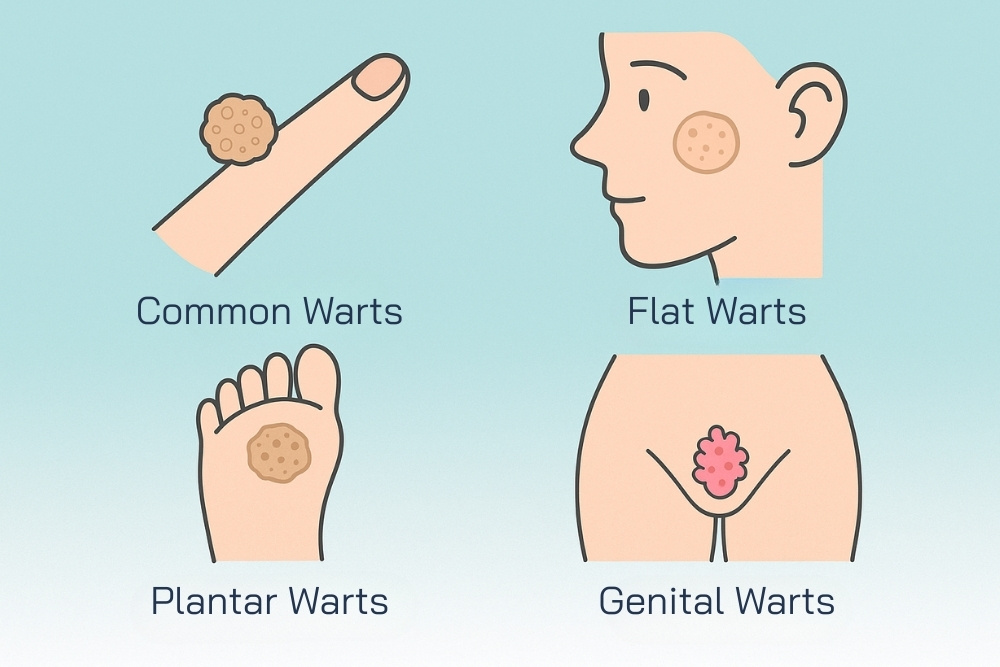
- Plantar Warts
- Caused by HPV types 1, 2, 4, and sometimes 63. These warts appear on the soles of the feet or palms of the hands, but they are most common on the feet. Unlike common warts that grow outward, plantar warts grow inward due to constant pressure and friction, making them painful when walking or standing.
- Genital Warts
- Characterized by soft, flesh-colored or pinkish growths that resemble a cauliflower or rooster’s comb. They can appear singly or in clusters around the genital area, anus, cervix, vagina, penis, or scrotum. Some people may not notice symptoms, while others may experience itching, burning, or abnormal discharge. Genital warts spread through direct skin-to-skin contact during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- Filiform Warts
- Caused by HPV types 10 and 20. These are finger-like projections of skin that extend outward, often found on the face, lips, neck, under the chin, or in areas with hair growth. They are usually flesh-colored or slightly pink and may cause mild itching or irritation. While they sometimes disappear on their own within months or years, cosmetic removal may be necessary.
2. Mucosal Warts
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Molluscum contagiosum is caused by the Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), a virus that spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact or by sharing personal items such as towels, nail clippers, or razors. These warts are characterized by small, dome-shaped bumps with a smooth, shiny surface and a distinctive central dimple. They typically measure 2–5 millimeters in diameter. Most cases are painless and not itchy, although mild itching can sometimes occur.
- Molluscum contagiosum can appear on various parts of the body, including the face, neck, chest, arms, legs, and genital area. In many cases, the lesions resolve on their own within 6–12 months as the immune system clears the virus. However, if the lesions persist or cause cosmetic concerns, medical treatment may be required.
- Oral Warts
- Oral warts are caused by HPV types 10 or 13 and present as small, raised bumps with a rough surface. They often have cracks or deep grooves in the center. These warts commonly appear on the lips, skin around the mouth, tongue, and the roof of the mouth (palate). While they are usually harmless, they can cause mild itching, discomfort, or pain.
- In many cases, oral warts may disappear naturally within a few months to several years. However, persistent or bothersome lesions, especially those that affect appearance or daily activities like eating and speaking, may require professional medical treatment. Because these warts are contagious, they can spread through direct contact with infected skin or indirectly through contaminated objects or surfaces. Preventive measures include avoiding close contact with infected individuals and not sharing personal items that can carry the virus.
Symptoms of Warts
The symptoms of warts from HPV vary depending on their type and where they appear on the body. In general, warts can cause discomfort, cosmetic concerns, or even pain. Below is a summary of the main types of warts and their common symptoms:

| Type of Wart | Characteristics & Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Common Wart (Verruca Vulgaris) | Hard, raised bump with a rough surface, usually small. Often found on hands or fingers. May cause mild itching or pain. |
| Flat Wart (Verruca Plana) | Small, flat, smooth bumps, flesh-colored or light brown. Often appear in clusters on the face, neck, arms, or backs of hands. Usually painless but can cause cosmetic concerns. |
| Plantar Wart (Verruca Plantaris) | Thick, hardened growth embedded in the skin. Painful when walking or standing. Typically found on the soles or heels, sometimes with tiny black dots. |
| Genital Wart (Condyloma Acuminata) | Soft, cauliflower-like growths, pink or flesh-colored, on the genital or anal area. May cause itching, burning, abnormal discharge, or bleeding during sex. |
| Filiform Wart | Thin, finger-like projections of skin, usually on the face, lips, or neck. Generally painless but may itch or cause irritation. |
| Molluscum Contagiosum | Small, dome-shaped bumps with a shiny surface and central dimple. Usually painless but can cause mild itching. Found on the face, neck, trunk, limbs, or genital area. |
| Oral Wart (Fissured Wart) | Small raised growths with grooves or cracks in the center. Found on lips, tongue, or the roof of the mouth. May cause mild itching or pain. |
Treatment for Warts
Although some warts from HPV can disappear on their own within 1–2 years as the immune system clears the infection, many cases cause discomfort, pain, or cosmetic concerns. This makes proper treatment important. Wart treatment is generally divided into two main categories: medication-based treatments and clinical procedures by a doctor.
Medication-Based Treatments for Warts
1. Salicylic Acid
- Mechanism: A keratolytic agent that gradually peels away the infected skin layer by layer until the wart is removed.
- How to use: Apply daily after soaking the affected skin in warm water and gently filing down the thickened surface.
- Time to see results: Usually 6–12 weeks of consistent use.
- Precautions: May irritate surrounding skin. Not recommended for young children or those allergic to the medication.
2. Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA)
- Mechanism: A strong acid that directly destroys wart tissue.
- Best for: Genital warts and warts in mucosal areas such as the mouth or genital region.
- Note: Should only be applied by a doctor. Incorrect use may cause skin burns and scarring.
3. Imiquimod Cream
- Mechanism: Stimulates the immune system to produce interferon and other immune responses to fight HPV.
- Best for: Genital and anal warts.
- How to use: Apply as prescribed by a doctor, several times per week for 4–16 weeks.
- Advantage: Lowers the risk of recurrence compared to removal methods alone.

Clinical and Specialist Treatments for Warts
1. Electrocautery
- Uses electric current to burn and destroy wart tissue.
- Suitable for large warts or those resistant to topical medication.
- Precaution: May cause scarring.
2. Cryotherapy
- Involves spraying liquid nitrogen onto the wart, freezing the tissue so it dies and falls off.
- Typically requires 1–3 sessions depending on the size and number of warts.
- Advantages: Quick, effective, and leaves minimal scarring.
- Side effects: Temporary pain, burning, or blistering after treatment.
3. Laser Therapy
- Uses concentrated laser energy to destroy the blood vessels feeding the wart, causing it to shrink and fall off.
- Ideal for warts that do not respond to other treatments or those located in deeper tissue.
- Advantages: Highly precise, reduces risk of viral spread.
- Precaution: More costly than other methods.
4. Minor Surgical Excision
- A small surgical procedure using a scalpel or special instrument to cut out the wart.
- Used for large warts or those resistant to all other treatments.
- Precaution: Carries risk of recurrence and potential scarring.
How to Prevent Warts from HPV
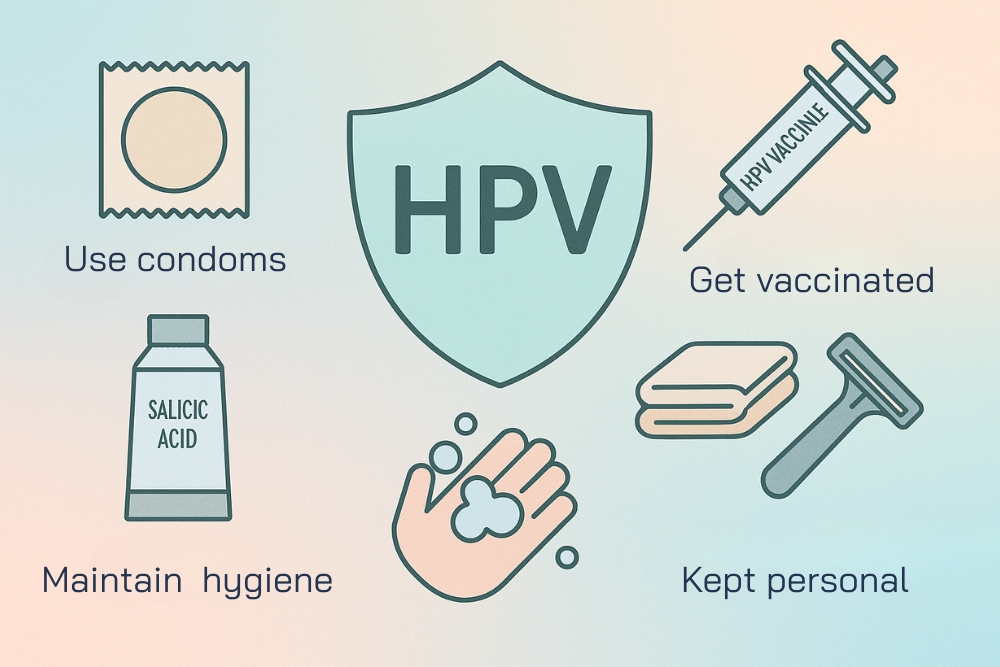
Preventing warts from HPV involves good personal hygiene, safe sexual practices, and protective measures. Here are some effective ways to reduce the risk of infection:
- Maintain proper hygiene: Shower at least twice a day and always dry your body thoroughly after bathing.
- Be cautious at salons or barbershops: Avoid nail salons or barbers that use unclean tools, especially when shaving hair or beards.
- Use condoms during sex: Consistent condom use helps lower the risk of HPV transmission, especially genital warts.
- Do not share personal items: Towels, clothes, shoes, socks, gloves, razors, and nail clippers should be kept personal. Sharing them can easily spread the virus.
- Limit sexual partners: Having multiple partners or frequent partner changes increases the risk of HPV exposure.
- Avoid direct contact with warts: Do not touch or scratch warts on others. If accidental contact occurs, wash your hands immediately with soap and water.
- Get vaccinated against HPV: The HPV vaccine is given in 2–3 doses (depending on the type). It has been proven to prevent genital warts by up to 90% and also protects against HPV-related cancers.
Herbal Remedies for Warts
While medical treatment is often the most effective approach, some people turn to herbal remedies as an alternative method to relieve symptoms and reduce discomfort. Commonly used herbs include:
- Euphorbia (Nipplewort / มะนมราชสีห์): Its latex contains antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. Apply the fresh sap directly to the wart daily to help it peel off over time.
- Holy Basil Leaves (กะเพรา): Known for antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Crush fresh leaves into a paste and apply regularly.
- Aloe Vera: The gel has soothing, antibacterial, and skin-healing properties. Apply daily to the affected area.
- Tamarind Bark: Contains natural acids that help exfoliate skin. Boil the bark in water, let it cool, and apply as a paste on the wart.
- Coconut Oil: Rich in antibacterial and anti-inflammatory compounds. Apply directly to the wart to reduce irritation and support healing.
How to Use Herbal Remedies for Warts
- Wash your hands thoroughly before and after touching warts.
- Clean the affected area with mild soap and water.
- Apply the chosen herbal remedy directly to the wart.
- Leave it on for about 30 minutes, then rinse with clean water.
- Repeat 2–3 times daily.
Consistent application for 2–3 weeks may help the wart to fall off. However, if the wart does not improve, worsens, or causes pain, you should consult a doctor for professional medical treatment.
Precautions When Using Herbal Remedies for Warts
- Discontinue use if allergic reactions occur: If redness, itching, or swelling develops after applying an herbal remedy, stop using it immediately.
- Avoid sensitive areas: Herbal remedies should not be applied near delicate areas such as the eyes or genitals.
- Consult a doctor if inflammation occurs: If the wart becomes painful, swollen, or shows signs of infection, professional medical advice is necessary.
While herbal remedies for warts are considered safe and may be effective, they often take longer to show results compared to conventional medical treatments. Still, they can be a natural alternative to help relieve discomfort and itching in mild cases.
Conclusion
Although warts (Warts from HPV) may appear to be harmless skin conditions, they are actually linked to the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), some strains of which can cause serious diseases such as cervical cancer, anal cancer, and oral cancer. Ignoring warts as if they were just small bumps that will disappear on their own may mean overlooking important warning signs from the body. Understanding the causes, symptoms, types of warts, treatment methods, and prevention strategies is therefore essential to protect yourself and those around you. Treatments for warts range from topical solutions and immune-boosting creams to clinical procedures such as cryotherapy, laser therapy, or minor surgical removal — depending on the location and severity of each wart.
“Equally important as treatment is prevention. The HPV vaccine is one of the most effective preventive measures, reducing the risk of genital warts by up to 90%, while also protecting against cancers related to HPV. Combined with proper personal hygiene, consistent condom use, and avoiding risky behaviors, vaccination significantly lowers the risk of infection. If you notice unusual skin changes — such as raised bumps, hardened lesions, pain, or abnormal growths, especially around the genital area — it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment not only improve outcomes but also reduce the risk of spreading the virus and help ensure that the condition is not a sign of something more serious.”
Ultimately, paying attention to your health and undergoing regular check-ups is the key to protecting yourself against warts and HPV-related diseases. Good health always begins with awareness and the right preventive measures.
Reference:
หูดธรรมดาที่พบได้บ่อย (Common warts)
เรื่องลับๆ ของผู้ชายที่ควรรู้เกี่ยวกับหูดหงอนไก่
- https://www.ram-hosp.co.th/news_detail/2650
รักษาหูดอย่างไรให้หายขาด
- https://www.siphhospital.com/th/news/article/share/496

